|
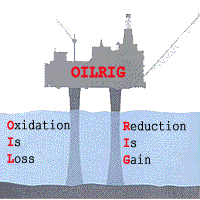
The terms oxidation number and oxidation state are often used interchangeably to indicate the apparent charge of an atom within a species. The IUPAC does differentiate between the two terms, representing oxidation numbers usign Roman numerals and oxidation states with numbers preceded by a sign. |
|
Oxidation state

The oxidation state this is the apparent valency of an atom within a compound.
This can be determined by treating all atoms as if they are ionic, to allow the apparent number of electrons gained or lost to be assessed.
The redox rules
- The sum of all the oxidation states in a compound must add up to 0.
- The sum of all of the oxidation states in an ion must add up to the charge on the ion.
- The oxidation state of an uncombined element is always zero (0).
- By convention, when naming compounds the oxidation number is written as a Roman numeral in the compound name immediately after the atom to which it refers.
|
Examples
|
Calculating the oxidation state
There are some elements that nearly always have the same oxidation state. These can be used to calculate the oxidation states of the atoms to which they are bonded.
Hydrogen, for example has an oxidation state of -1 when bonded to a metal (more electropositive element) and +1 when bonded to a more electronegative element (non-metal). Oxygen is nearly always -2 (the exception is when it is in the form of the peroxide ion, O-O2-, it has an oxidation state of -1).
Group 1 and 2 metals have an oxidation state of +1 and +2 respectively.
|
Example: Calculate the oxidation state of sulfur in sulfuric acid H2SO4
(2 x H) + S + (4 x O) = 0 2 + S - 8 = 0 S = +6 |
|
Example: Calculate the oxidation state of nitrogen in calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2
Therefore: (+2) + [(2 x N) + (6 x -2)] = 0 +2 + 2N -12 = 0 2N = 10 N = +5 |
Oxidation state in ions
When you are dealing with an ion, the process for working out the oxidation state of the atoms within the ion is the same, with the important exception that the sum of the oxidation states must add up to the charge on the ion.
|
Example: Calculate the oxidation state of the chloride atom in the chlorate ion, ClO3- Each of the oxygen atoms has an oxidation state of -2 Therefore as Cl + (3 x -2) = -1 Then Cl = -1 + 6 = +5 |