|
A chemical change may be defined as: "A process in which a new substance is formed" |
|
The particulate nature of chemical reactions
All substances are characterised by particles of a specific type and composition. This means that for a chemical change to occur there must be a change occurring in the smallest particles of the substances.
In chemical compounds the particles are held together by chemical bonds, either covalent or ionic. For reaction to occur these bonds must be broken and other bonds formed.
For bonds to be broken there must be collisions between particles. This collision is necessary to provide enough energy to break the bonds and initiate the reaction.
However, the numbers of atoms making up the particles involved in the reactions cannot change. If there are a total of 6 atoms before reaction, however they are arranged, there must be a total of 6 atoms after the reaction - particles cannot simply disappear or appear - that would be magic!
The reaction between hydrogen and oxygen
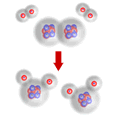
When hydrogen reacts with oxygen to produce water the original reactants are molecules of hydrogen and oxygen. These consist of atoms held together by covalent bonds to form H2 and O2 molecules.
These molecules must physically collide in order to break the bonds holding the atoms together in the molecule, before new bonds can be formed. The new bonds that are formed between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms hold the atoms together in a ratio of two hydrogen atoms for each oxygen atom.
We call this arrangement of atoms a water molecule!
In terms of reacting particles, one molecule of oxygen must react with two molecules of hydrogen for the process to make two molecules of water.
In terms of moles of particles, this equates to one mole of oxygen molecules reacting with two moles of hydrogen molecules making two moles of water molecules.
The number of reacting particles is shown by the coefficients of the equation (the large numbers that appear in front of the chemical formulae in the balanced equation)
|
oxygen + hydrogen
O2 + 2H2
|